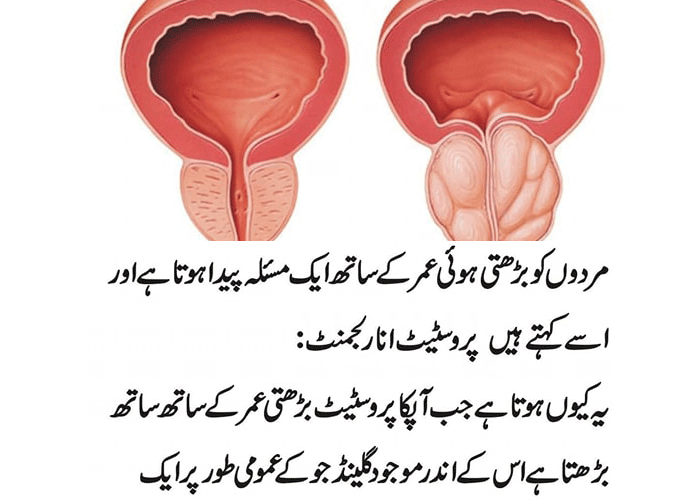
Introduction
Prostate health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being for men, especially as they age. Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men worldwide, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is vital. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of prostate cancer, helping you recognize early signs and explore various treatment pathways.
Understanding the Prostate
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It plays a key role in male reproductive health by producing seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. As men age, the prostate can undergo various changes, including enlargement and the development of cancerous cells.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer’s exact causes remain unclear, but several factors contribute to its development.
Genetic Factors



A family history of prostate cancer significantly increases the risk. Mutations in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, also contribute to higher susceptibility.
Environmental Influences
Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. Research is ongoing to pinpoint specific environmental triggers.
Lifestyle Factors
Diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle habits can influence prostate cancer risk. Diets high in red meat and low in fruits and vegetables have been linked to a higher incidence of prostate cancer.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of prostate cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Early-Stage Symptoms
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Painful or burning urination
Advanced-Stage Symptoms
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pain in the hips, back, or chest
- Weakness or numbness in the legs or feet
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Age
The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, particularly after age 50.
Family History
Having a close relative with prostate cancer significantly raises your risk.
Race and Ethnicity
African-American men are more likely to develop prostate cancer than men of other races, and they often develop it at a younger age.
Diet and Lifestyle
A diet high in red meat and dairy products and low in fruits and vegetables can increase the risk. Obesity and lack of physical activity also contribute to higher risk.
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment.
Screening Tests
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures the level of PSA in the blood.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): Physical examination of the prostate.
Diagnostic Procedures
- Biopsy: Removal of a small tissue sample for examination.
- Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, and bone scans to assess cancer spread.
Staging and Grading of Cancer
Staging determines the extent of cancer, while grading assesses how much the cancer cells differ from normal cells.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Various treatment options are available depending on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer.
1. Active Surveillance
Who is it for? Men with low-risk, slow-growing prostate cancer.
Benefits and risks: Avoids overtreatment, but requires regular monitoring.
2. Surgery
Types of surgical procedures:
- Radical Prostatectomy: Removal of the entire prostate.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive approach.
Recovery and outcomes: Varies by individual, with possible side effects including urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
3. Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation: Targets cancer cells with high-energy rays.
Brachytherapy: Implants radioactive seeds directly into the prostate.
4. Hormone Therapy
Purpose and methods: Reduces levels of male hormones to slow cancer growth.
Side effects and considerations: Can cause hot flashes, reduced libido, and bone thinning.
5. Chemotherapy
When it’s used: For advanced prostate cancer not responding to other treatments.
Common drugs and side effects: Includes drugs like docetaxel; side effects can be severe, including nausea and hair loss.
6. Immunotherapy
How it works: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
New developments: Research is ongoing, with promising new treatments emerging.
7. Targeted Therapy
What makes it different: Targets specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Examples of targeted drugs: PARP inhibitors and other novel agents.
Managing Side Effects of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Common side effects: Urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and gastrointestinal issues.
Coping strategies: Pelvic floor exercises, medications, counseling, and support groups.
Support resources: Access to healthcare professionals, patient support groups, and counseling services.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Factors influencing prognosis: Stage of cancer, patient’s overall health, and response to treatment.
Survival statistics: Prostate cancer has a high survival rate, especially when detected early.
Importance of early detection: Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve outcomes.
Preventing Prostate Cancer
Lifestyle changes: Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
Dietary recommendations: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Regular screening: Discuss with your doctor about starting screenings at age 50, or earlier if you have risk factors.
Living with Prostate Cancer
Emotional and psychological impact: Coping with a cancer diagnosis can be challenging.
Support systems and resources: Family, friends, support groups, and professional counseling can help.
Quality of life considerations: Focus on maintaining a good quality of life through treatment and beyond.
Conclusion
Understanding prostate cancer, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take proactive steps towards maintaining your health. Regular screenings and a healthy lifestyle are key to early detection and effective management of prostate cancer.