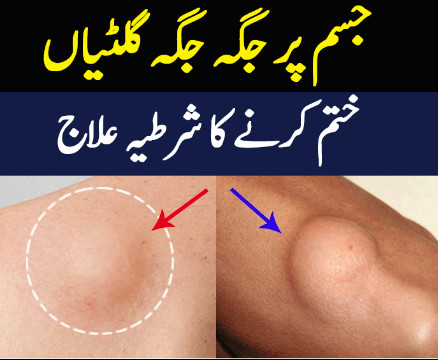
Lipomas are benign tumors composed of adipose tissue, commonly found just beneath the skin. While lipomas are generally harmless and rarely cause serious health issues, understanding their symptoms and treatment options is essential for proper management. In this article, we’ll explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of lipomas.
Introduction
A lipoma is a slow-growing lump or mass that develops between the skin and the underlying muscle layer. These fatty tumors are typically soft to the touch, movable, and painless. While lipomas can develop anywhere on the body, they most commonly occur on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, or thighs.
Symptoms of Lipoma
Lump or Mass
The primary symptom of a lipoma is the presence of a soft, doughy lump or mass beneath the skin. Lipomas are usually small, ranging from pea-sized to several centimeters in diameter, although they can grow larger over time.
Painlessness
Unlike other types of tumors or cysts, lipomas are typically painless and may only cause discomfort if they press against nearby nerves or organs.
Movable
Lipomas are usually movable when touched and can be pushed slightly under the skin. This characteristic helps differentiate them from other types of growths that may be fixed or attached to deeper tissues.
Slow Growth
Lipomas tend to grow slowly over time, often remaining stable in size for years or even decades. Rapid growth or sudden changes in size may indicate a different type of tumor and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Treatment of Lipoma
Observation
In many cases, lipomas are asymptomatic and do not require treatment. If the lipoma is small, painless, and not causing any functional impairment, a “wait and watch” approach may be recommended.
Surgical Removal
For cosmetic reasons or if the lipoma causes discomfort or affects nearby structures, surgical removal may be necessary. This procedure, known as excision, involves making an incision over the lipoma and removing the tumor along with surrounding tissue.
Liposuction
In some cases, liposuction may be used to remove larger lipomas or those located in areas where surgical excision may be challenging. During liposuction, a thin tube (cannula) is inserted into the lipoma, and the fatty tissue is suctioned out.
Steroid Injections
Steroid injections may be used to reduce the size of lipomas or alleviate symptoms such as inflammation or discomfort. These injections can help shrink the lipoma by reducing inflammation and inhibiting the growth of fatty tissue.
Lipoma Removal at Home
While it’s not advisable to attempt to remove a lipoma at home, certain natural remedies such as apple cider vinegar, turmeric, or chickweed may be applied topically to help reduce inflammation and shrink the tumor. However, these methods have not been scientifically proven and may not be effective for all individuals.
Conclusion
Lipomas are benign tumors composed of fatty tissue that typically develop just beneath the skin. While lipomas are generally harmless and may not require treatment, surgical removal may be necessary if they cause discomfort, affect nearby structures, or for cosmetic reasons. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management of lipomas.